CSS 面试点总结
简介
Cascading Style Sheets,层叠样式表
- CSS 层叠样式表 - MDN
- CSS Object Model(CSSOM)CSS对象模型 - MDN
- CSS HOME - w3c
常见面试题
基础核心
- 盒模型
- margin 重叠是什么?如何解决?
- BFC?如何触发?能解决什么问题?
- display 的常见值
- position 的常见值
- z-index 层叠上下文
选择器
- 常见选择器
- 伪类、伪元素
- 优先级(权重)
- 浏览器选择器匹配原理
- 为什么不建议用过深的选择器
布局
- float
- flex
- grid
响应式
- 媒体查询(@media)
- px、em、rem、vw、vh、% 的区别?
- 移动端适配方案有哪些?
动画与过渡
- CSS 动画(animation)与 transition 的区别?
- GPU加速 涉及哪些 CSS 属性(transform、opacity 等)?
- will-change 是做什么的?为什么慎用?
工程化
- 模块化
- 预处理器
- 样式隔离
- Tailwind CSS 的核心思想是什么?为什么它越来越流行?
渲染性能
- 浏览器的渲染流程
- 为什么说 CSS 是阻塞渲染的?
- Reflow(回流/重排)和 Repaint(重绘)的区别?
- 如何处理 CSS 优化
实践应用
- 垂直居中和水平居中
- 两栏布局、三栏布局
- 如何实现一个 1px 边框 的问题(尤其在 Retina 屏下)
- 如何实现文字超出显示省略号(单行、多行)?
- 实现一个三角形 / 扇形 / 梯形等图形的 CSS 原理?
- 如何实现自适应正方形/圆形块?
其他
- 哪些 CSS 属性可以继承?
- line-height 如何继承?为何常用无单位写法?
- 为什么 vertical-align: middle 经常不起作用?
- display: none、visibility: hidden 和 opacity: 0 的区别?
盒模型
一个盒子由四个部分组成:content padding border margin
box-sizing 用来控制元素的盒子模型的解析模式,默认为 content-box
context-box:标准盒模型,默认
设置的height/width = content
盒子的宽/高 = width/height + padding + border
border-box:替代盒模型
设置的height/width = content + padding + border
盒子的宽/高 = width/height
⚠️ margin 不属于元素本身的宽高,但在计算元素占用的空间时会包含 margin。
参考
- CSS 基础框盒模型介绍 - MDN
- 盒模型 - MDN
外边距重叠
垂直方向上,两个相邻块级元素的 margin 会合并成一个新的 margin 值。
计算规则
- 正正取大
- 上边 margin-bottom: 20px,下边 margin-top: 30px
- 间距为 30px
- 一正一负相加
- 上边 margin-bottom: -20px,下边 margin-top: 30px
- 间距为 10px
- 负负取绝对值大(即取更小的那个)
- 上边 margin-bottom: -20px,下边 margin-top: -30px
- 间距为 -30px
常见场景
- 相邻兄弟元素之间的 margin 会重叠
- 父元素与第一个/最后一个子元素之间 margin 会重叠
- 空元素自身的上下 margin 会互相重叠
<div class="a">ddd</div>
<!-- 30px -->
<div class="b">ddd</div>
<style>
.a {
margin-bottom: 30px;
}
.b {
margin-top: 20px;
}
</style>
<!-- 30px -->
<div class="parent">
<div class="child"></div>
</div>
<style>
.parent {
margin-top: 20px;
}
.child {
margin-top: 30px;
}
</style>
<div>ddd</div>
<div class="empty"><!-- 30px --></div>
<div>ddd</div>
<style>
.empty {
margin-top: 30px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
</style>解决方法
父子重叠:
- 触发父元素 BFC
- display: flow-root;
- overflow: hidden;
- 给父元素加 padding或border
- 使用伪元素
兄弟重叠:
- 调整数值
- 其中一个包裹在触发 BFC 的容器中
参考
BFC
Block Formatting Context,块级格式化上下文。
它是一个独立的渲染区域,内部元素和外部元素互不影响。
创建BFC:
- html
- float: left、right
- position: absolute、fixed
- overflow: hidden、scroll、auto
- display
- flex/inline-flex
- grid/inline-grid
- inline-block
- table、table-*、inline-table
- flow-root
- column-count、column-width、column-span
- contain: size、layout、paint
🆕 flow-root:这是 CSS3 新增的属性,专门用来触发 BFC,且没有副作用(不会像 overflow: hidden 那样可能裁切内容)。
特性:
- BFC 内部的盒子垂直方向从上到下排列
- 同一个 BFC 内部的相邻元素会发生 margin 合并
- BFC 之间不塌陷,这就是 BFC 能阻止 margin-collapse 的原因。
- 浮动元素(float)不会覆盖 BFC 的布局区域
- BFC 会包含内部浮动元素(高度不塌陷)
作用:
① 避免外边距(margin)重叠
父子、兄弟元素的 margin 本该塌陷,通过触发 BFC 可以阻止。
<div class="box">box</div>
<!-- 40px -->
<div class="container" style="overflow: hidden;">
<div class="box">box</div>
</div>
<!-- 40px -->
<div class="box">box</div>
<!-- 20px -->
<div class="box">box</div>
<style>
.box {
margin: 20px 0;
}
</style>② 解决高度塌陷(清除浮动)
浮动元素不占高度,导致父容器高度塌陷;
触发 BFC 的容器可以包裹浮动元素,恢复高度。
<div class="parent">
<div class="child"></div>
</div>
<style>
.parent {
/* 触发 BFC,解决高度塌陷 */
overflow: hidden;
/* 或者 */
display: flow-root;
background: gray;
}
.child {
float: left;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
</style>③ 阻止文本环绕(让浮动元素不影响旁边布局)
BFC 区块不会与 float 元素重叠,会出现在其旁边或下面。
<div class="float-box"></div>
<div class="text">
文本不会再环绕浮动元素,因为 text 这个盒子形成了新的 BFC。 新的 BFC 会避开
float 形成的影响,而是整体避让浮动元素。 因此这段文本会被“挤到下方”。
</div>
<style>
.float-box {
float: left;
width: 30px;
height: 30px;
margin-right: 12px;
background: #4aa3ff;
}
.text {
/* 创建 BFC */
overflow: hidden; /* 或者 */
display: flow-root;
background: #f0f0f0;
}
</style>参考
- BFC - MDN
- Introduction to formatting contexts 格式化上下文简介 - MDN
display
参考
- display - MDN
position
- static:正常的文档流,
- relative:相对定位,相对于其父级元素
- absolute:绝对定位,脱离文档流,以最近的不是static的父级元素为参考
- fixed:绝对定位,以浏览器窗口作为参考
- sticky:粘性定位,relative和fixed的混合
参考
z-index
z-index 属性决定了元素在页面 Z 轴(垂直于屏幕方向)上的堆叠顺序。简单来说,它决定了哪个元素盖在哪个元素上面。
- 每个上下文内部有自己的绘制顺序,外部上下文无法穿透进去与其子元素竞争绘制优先。
- z-index 只在同一个层叠上下文(stacking context)内比较。
创建新的层叠上下文
常见的:
- 根元素 html
- position
- 为 absolute 或 relative 且 z-index 不为 auto 的元素
- position 为 fixed 或 sticky 的元素
- display: flex/grid 的子元素, 且 z-index 值不为 auto
- opacity < 1
- transform 不是 none
更多的CSS3 新属性的情况,参考:MDN - 层叠上下文
层叠顺序
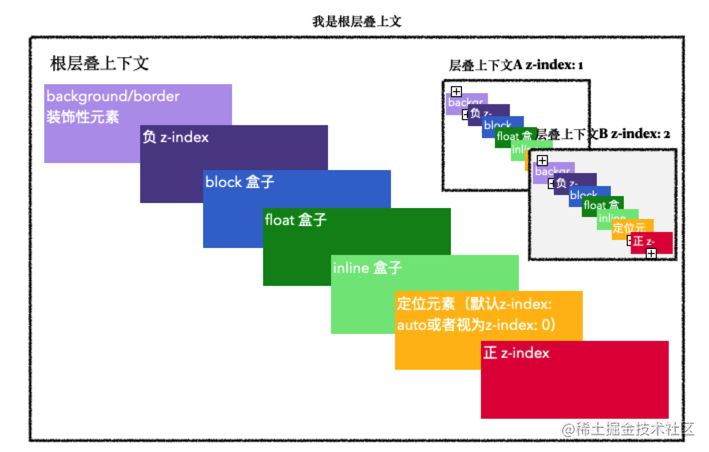
- 背景和边框:层叠上下文所属元素的 background 和 border(最底层)
- 负值 z-index:z-index < 0 的子元素
- 块级盒子:普通文档流中的 block 块级元素(用于布局)
- 浮动盒子:float 元素(非 none)
- 行内盒子:普通文档流中的 inline/inline-block 盒子(文字内容)
- z-index: 0 或 auto:定位元素(position 非 static),但没有设置正数 z-index
- 正值 z-index:z-index > 0 的子元素
z-index 相同:在 HTML 代码中后出现的元素在上。
Within each stacking context, the following layers are painted in back-to-front order:
- the background and borders of the element forming the stacking context.
- the child stacking contexts with negative stack levels (most negative first).
- the in-flow, non-inline-level, non-positioned descendants.
- the non-positioned floats.
- the in-flow, inline-level, non-positioned descendants, including inline tables and inline blocks.
- the child stacking contexts with stack level 0 and the positioned descendants with stack level 0.
- the child stacking contexts with positive stack levels (least positive first).
为什么 z-index 不生效
- 没加定位:元素是 static(默认),z-index 对其无效。
- 拼爹失败:父元素创建了层叠上下文,且父元素的 z-index 很低。子元素再高也没用。
- CSS3 属性干扰:父元素设置了 opacity < 1 或 transform,导致父元素变成了层叠上下文,限制了子元素的层级提升。
参考
- 理解 CSS 的 z-index 属性 - MDN
- z-index - W3C
选择器
- 通配符
* - id选择器
#box - 类(class)选择器
.wrapper - 标签选择器
h1div - 关系/组件选择器
- 后代选择器
,box .title,儿子、孙子… - 子代选择器
.box > .title,儿子 - 相邻兄弟选择器
h1 + p,后面的第一个兄弟 - 通用兄弟选择器
h1 ~ p,后面所有的兄弟
- 后代选择器
- 属性选择器
- [attribute] 选择带有attribute属性的元素
- [attribute=value] 完全匹配
- [attribute~=value]
p[class~="special"]包含单词 - [attribute*=value]
div[class*="box-"]包含子串 - [attribute^=value] 以…开头
- [attribute$=value] 以…结尾
- [attribute|=value]
div[lang|="zh"]
- 伪类选择器
a:hover - 伪元素选择器
.box::after - 群组选择器
div, p
伪类
用于选择元素的特定状态或位置
伪类列表 - MDN
部分:
:hover:last-child:first-child:nth-child(n):is(selector):where(selector):has(selector):not(selector)
伪元素
用于选中元素的特定部分,或者创建虚拟元素。
伪元素列表 - MDN
部分:
::before::after::first-letter::first-line::selection
参考
- 伪类和伪元素 - MDN
优先级权重
🚩 !important > 内联 > 优先级计算值
🚩 优先级相同时,显示后面的样式
三个不同的值相加,百(ID)十(类)个(元素)—— 三位数的三个位数
- 100:id
- 10:类、属性、伪类
- 1:标签、伪元素
- 0:通配符
*、组合/关系符号 + > ~,权重为 0,不影响优先级。
特殊情况:
- :is():取内部最高权重
- :not():取内部最高权重
- :has():取内部最高权重(非常强大)
- :where():优先级永远是 0,不管里面写什么
| 选择器 | ID | 类 | 标签 | 优先级 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| h1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0-0-1 |
| h1 + p::first-letter | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0-0-3 |
| li > a[href*=“en-US”] > .inline-warning | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0-2-2 |
| #identifier | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1-0-0 |
| button:not(#mainBtn, .cta) | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1-0-1 |
比较规则:
- 从左往右依次进行比较 ,较大者优先级更高
- 如果相等,则继续往右移动一位进行比较
- 如果所有位全部相等,则后面的会覆盖前面的
🚨 注意:低等级的选择器数量再多,也无法超越高等级。
例如 100 个 class 叠加 (0, 100, 0) 也比不上 1 个 ID (1, 0, 0)
浏览器解析
❓ 浏览器是如何解析 CSS 选择器的?
✅ 浏览器从右向左匹配选择器
例子:div .box span
- 浏览器先找到页面上所有的 span。
- 然后向上查找,看它的父级是不是 .box。
- 如果是,再向上查找是不是 div。
原因:从右向左(先找子元素)能更快地过滤掉不符合条件的路径,效率比从左向右(先找根元素再向下遍历)高。
不使用过深的选择器
- 性能问题
- ✔ 深选择器 ≠ 性能灾难
- ❌ 但确实会增加每个元素的“祖先链检查成本”
- 可维护性差
- 太依赖 DOM 结构,只要 HTML 结构稍改,样式就可能失效。
- 难以阅读(语义不清晰)
- 权重难控制
参考
- CSS 选择器 - MDN
- CSS 选择器 - MDN
- 层叠、优先级与继承 - MDN
- 优先级计算 - MDN
- 层叠层 @layer - MDN
float
特性
- 脱离标准文档流
- 浮动的元素变成行内块,在一行显示
浮动带来的问题
- 父元素的高度无法被撑开
- 影响其他元素
清除浮动
- clear
- 增加同级空标签
- 父元素伪元素 ::after
- BFC
- 父元素设置 overflow
- 父元素设置 display: flow-root
参考
- 浮动 - MDN
flex
响应式
工程化
动画
animation是动画属性,它的实现不需要触发事件,设定好时间之后可以自己执行,且可以循环一个动画。transition是过度属性,强调过度,它的实现需要触发一个事件(比如鼠标移动上去,焦点,点击等)才执行动画。
多数显示器默认频率是60Hz,即1秒刷新60次,所以理论上动画最小间隔为1/60*1000ms = 16.7ms。
参考
- CSS动画 animation - MDN
- 使用 CSS 动画 animation - MDN
- 使用 CSS 过渡 transition - MDN
- requestAnimationFrame - MDN
属性继承机制
给父元素设置了某些样式属性,子元素会自动拥有这些属性,而不需要在子元素上重新写一遍。
💛 默认继承
主要与文字内容的显示有关。
- 字体
- font(简写)
- font-family(字体族)
- font-weight(粗细)
- font-size(大小)
- font-style(斜体等)
- font-variant(小型大写字母)
- 文本
- color(文本颜色)
- line-height(行高)⚠️ 继承但有特殊计算机制
- text-align(文本对齐方式)
- text-indent(首行缩进)
- text-transform(大小写转换)
- letter-spacing(字间距)
- word-spacing(单词间距)
- white-space(换行处理)
- direction(文字方向(ltr/rtl))
- 列表
- list-style
- list-style-type(如 disc, circle, decimal)
- list-style-image
- list-style-position
- 表格
- border-collapse(边框合并)
- border-spacing(边框间距)
- caption-side(标题位置)
- empty-cells(显示空单元格)
- visibility:父元素 visibility: hidden,子元素也会隐藏。但如果给子元素单独设置 visibility: visible,子元素可以显示出来。
- cursor:鼠标样式
💛 默认不继承
主要与元素的尺寸、定位、背景有关。
- 盒模型:width, height, margin, padding, border
- 背景:background
- 定位与布局:position, top/right/bottom/left, z-index, float, display, overflow
- vertical-align
- opacity
🎈 父元素设置了背景色,子元素看起来也有背景色。
子元素的 background-color 默认值是 transparent(透明),所以你透过子元素看到了父元素的背景
🎈 父元素 opacity: 0.5,子元素也会变半透明。
这其实不是属性继承,而是层叠上下文的影响。父元素作为一个整体变透明了,里面的子元素自然也跟着变了。你无法通过给子元素设置 opacity: 1 来让它变回不透明
💛 控制继承
- inherit:某个本来不继承的属性(比如 border)也能从父元素那里继承
line-height?为何常用无单位写法?
line-height 指的是两行文字基线 (baseline) 之间的垂直距离。
line-height 控制行框的高度,多余的空间平均分布在文字上下。
单行文本设 line-height 等于 height。
- 有单位(px, %, em):继承的是计算后的绝对像素值。
- 无单位(1.5):继承的是比例系数,子元素会根据自己的 font-size 动态计算。
参考
为什么 vertical-align: middle 经常不起作用?
💡 属性只对行内级元素(inline、inline-block)和表格单元格(table-cell)生效。
💡 它让元素的“中线”与父行框的“中线”对齐,而不是让元素在父容器垂直居中。
💡 它不是用来垂直居中块元素的。
参考
- vertical-align - MDN
display: none、visibility: hidden、opacity: 0 的区别
| display: none | visibility: hidden | opacity: 0 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 可见性 | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| 占据空间 | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| 重排/回流 | Reflow (回流) | Repaint (重绘) | 配合 GPU 加速(硬件加速) |
| 点击/触发事件 | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
| 子元素显隐 | ❌ | ✅子元素设为 visible 可见 | ❌ |
| 过渡动画 | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
场景推荐
- 完全移除元素(如 Tab 切换未选中的面板):用 display: none。
- 需要保留位置,但不想要响应事件(如加载占位符):用 visibility: hidden。
- 制作淡入淡出动画,或者看起来隐藏但依然需要点击(如覆盖在图片上的透明点击层):用 opacity: 0。
收藏文章
- 干货!各种常见布局实现+知名网站实例分析 - 掘金